Cocoa production in Africa
 Where does cocoa come from?
Where does cocoa come from?
Cocoa is the essential ingredient for our chocolate.
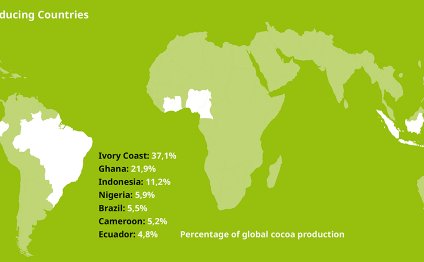
It originates from the seeds (cocoa beans) of the cocoa fruits (cocoa pods), which grow on cocoa trees. The production of cocoa begins in the tropical regions around the Equator, where the hot and humid climate is well suited for growing cocoa trees. 70% of the world’s cocoa beans come from four West African countries: Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria and Cameroon. The Ivory Coast and Ghana are by far the two largest producers of cocoa: together they cultivate more than half of the world´s cocoa. These two are followed by other cocoa producing countries like Indonesia, Nigeria, Cameroon, Brazil and Ecuador.
Worldwide, 90% of cocoa is grown on small family farms of 2 to 5 hectares, while just 5% comes from large plantations of 40 hectares or more. Cocoa production provides livelihoods for between 40 and 50 million farmers, rural workers and their families in the Global South. In the Ivory Coast and Ghana up to 90% of the farmers rely on cocoa for their primary income.
 From trees to sacks
From trees to sacks
Growing cocoa is hard manual work and very labour intensive, as caring for and harvesting the beans requires close and continuous attention. The cocoa tree flowers and bears fruit throughout the entire year. It produces large cocoa pods, which need to be cut from the trees by machetes or sticks. Each cocoa pod contains around 20 to 30 seeds sitting in a sweet white pulp – these are the actual cocoa beans. It takes a whole year’s crop from one tree to make half a kilo of cocoa. As pods do not ripen at the same time, the trees need to be monitored continuously. Cocoa is also a very delicate crop, easily affected by changes in weather and susceptible to diseases and pests. After the harvest, the ripe pods need to be cut open with machetes and the beans are taken out. The cocoa beans then need to be fermented, dried, cleaned and packed. When the beans are packed into cocoa sacks, the farmers are ready to sell the product to intermediaries.
From sacks to butter
Intermediaries buy the sacks of unprocessed beans and sell them to exporters. When the beans reach the grinding companies in the global North, the cocoa still needs to be processed. The beans are crushed and the shells removed, roasted, and finally ground. The result – cocoa liquor – is used to manufacture chocolate, or is further processed for cocoa butter and cocoa powder.
RELATED VIDEO



Share this Post
Related posts
Oil production in Africa
Africa as a continent is home to a number of the world’s fastest-growing economies, a lot of them buoyed by fresh oil and…
Read MoreSustainable Agriculture in Africa
WWF-SA engages in efforts to promote sustainable agriculture, minimise adverse impacts of farming on the environment and…
Read More










